Preventive health measures are pivotal in sustaining long-term health and wellness, particularly for women. As Benjamin Franklin famously said, “An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.” This adage holds especially true in women’s health, where early intervention can prevent many health issues later in life. By prioritizing preventive care, women can enhance their quality of life and ensure they remain active and healthy for years to come.
Preventive health refers to the steps, screenings, and habits to prevent diseases before they start. For women, this means managing risk factors and undergoing regular screenings tailored to female health needs. Preventive health is crucial because it helps detect potential health issues early, offers a chance for timely intervention, and reduces the overall burden of diseases in women’s lives.
Regular Health Screenings
Health screenings are a cornerstone of preventive health for women. Essential screenings include:
-
Mammograms to detect breast cancer are recommended annually or biennially for women aged 40 and above.
-
Pap smears to catch early signs of cervical cancer are suggested every three years for women starting at age 21.
-
Bone density scans for osteoporosis are particularly important for postmenopausal women or those at high risk.
Each of these screenings plays a critical role in early detection, which can significantly alter the course of treatment and increase the likelihood of positive outcomes. Regular scheduling based on age and risk factors ensures that women are not only aware of their current health status but also take proactive steps to maintain it over time.
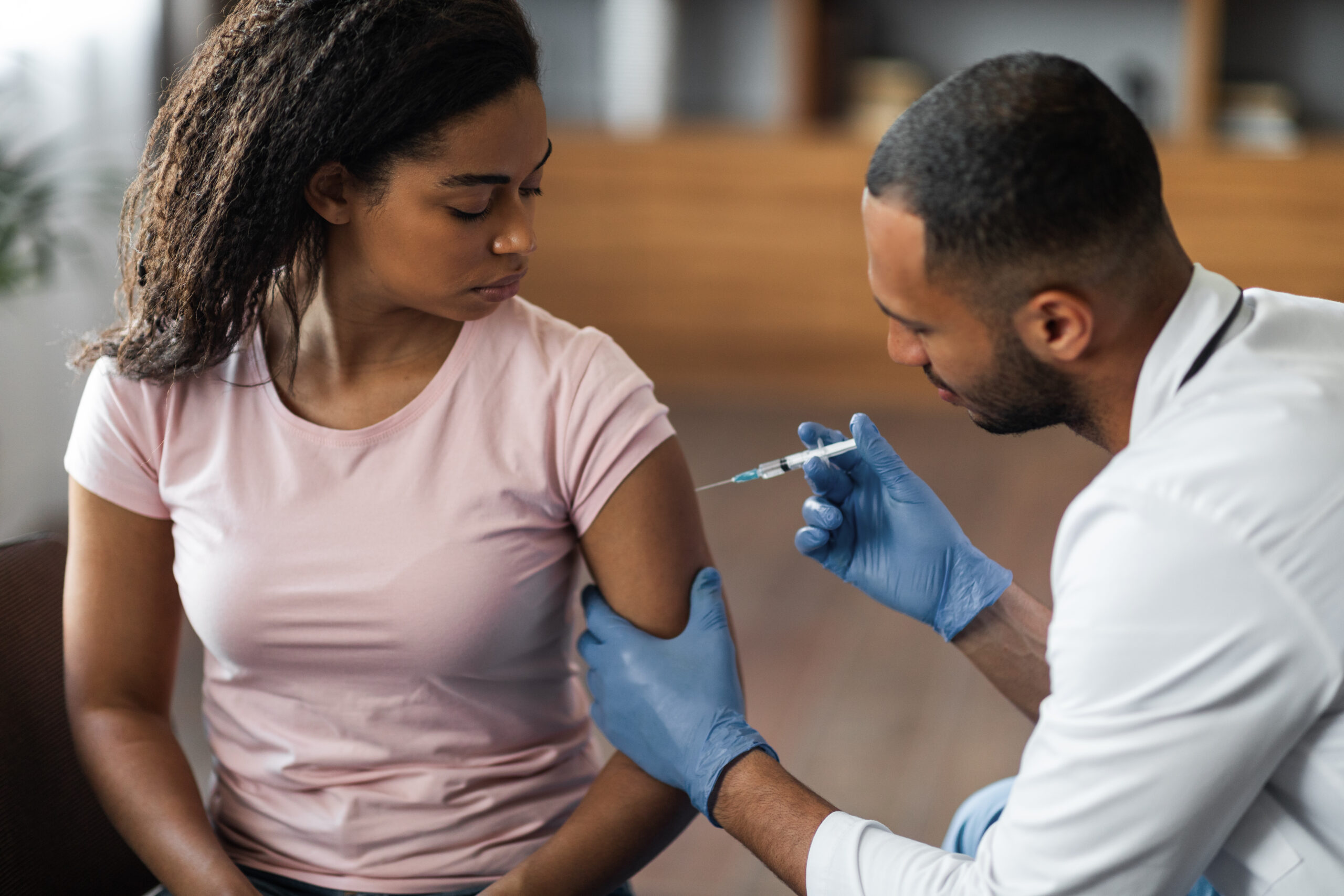
Vaccinations
Vaccinations are key preventive tools that protect against serious diseases. Essential vaccines for women include the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, which can prevent cervical cancer, and the seasonal flu shot, which is crucial for maintaining health, especially in women with underlying health conditions or those who are pregnant.
-
The HPV vaccine is recommended for girls and women ages 9 to 26 to protect against the strains of HPV most likely to cause cervical cancer.
-
The Tdap vaccine (tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis) is important for women of all ages, especially pregnant women, to protect both mother and newborn from pertussis.
-
Annual flu vaccines are recommended for all women, particularly those older or with chronic health issues.
Integrating these preventive measures into regular health care empowers women to take charge of their health and supports a healthier society by reducing the prevalence and impact of preventable diseases. By addressing these foundational aspects of women’s health care, women can lead more active lives.
Nutritional Supplements
For many women, nutritional supplements are crucial in maintaining optimal health and filling dietary gaps. Key supplements include:
-
Calcium: Essential for bone health, particularly important as women age and their risk for osteoporosis increases.
-
Iron: Crucial for women of childbearing age to compensate for iron loss during menstruation.
-
Vitamin D: Supports bone health and immune function and can be especially important in regions with limited sunlight exposure.
-
Folic Acid: This is vital for pregnant women or those planning to become pregnant, as it helps prevent neural tube defects in the fetus.
Supplementing these nutrients can prevent common deficiencies that may lead to health issues such as anemia, bone density loss, and developmental problems in pregnancy. “Let thy food be thy medicine,” said Hippocrates, underscoring the importance of nutrients in maintaining health. When diet alone isn’t enough, supplements can play a pivotal role in ensuring women receive the nutrients they need.
Mental Health Assessments
Mental health is as critical as physical health, yet it often does not receive the same attention. Regular mental health assessments can help detect issues like depression, anxiety, and stress early, which is crucial for timely and effective treatment. “There is no health without mental health” highlights the integral role mental health plays in overall well-being.
Women can access mental health screenings through their primary healthcare providers, mental health professionals, or even through digital health services. Many online platforms now offer self-assessment tools that can guide women to understand their mental health status and seek appropriate care. Regular assessments should be part of an annual health check-up to maintain mental well-being.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle choices play a fundamental role in maintaining health. A balanced diet rich in nutrients, regular physical activity, and effective stress management techniques are all essential for good health. Each component supports physical wellness and contributes significantly to mental and emotional well-being.
-
Diet: Incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains into daily meals. Planning meals can help maintain a balanced diet and avoid unhealthy choices.
-
Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week, combined with muscle-strengthening exercises two or more days a week.
-
Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and regular social interactions can reduce stress. Setting aside time for hobbies and relaxation is also crucial.
 Implementing these lifestyle modifications can lead to significant improvements in health, enhancing both quality of life and longevity. Encouraging women to make informed choices about their health can empower them to lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Implementing these lifestyle modifications can lead to significant improvements in health, enhancing both quality of life and longevity. Encouraging women to make informed choices about their health can empower them to lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Genetic Testing and Counseling
Genetic testing and counseling offer transformative benefits by providing insights into one’s genetic predispositions to certain health conditions. For women, this can include hereditary cancers such as breast and ovarian cancer, heart disease, and other genetic disorders. Understanding these risks early on allows for proactive measures and personalized health strategies. As the saying goes, “Forewarned is forearmed,” meaning knowledge of one’s genetic makeup can be a powerful tool in preventive health care.
With the knowledge gained from genetic testing, women can work with healthcare providers to develop targeted prevention plans. This might include more frequent screenings, preventive medication, lifestyle adjustments, or even preventive surgeries in high-risk cases. Such personalized care plans significantly enhance the ability to manage potential health risks effectively.
Community Health Initiatives
Community resources and programs support women’s health by providing accessible health services, education, and support networks. These resources might include free or low-cost screening programs, educational workshops, and support groups catering to women’s health needs. Community health initiatives often serve as the first defense against health disparities, especially in underserved areas.
Community initiatives enhance access to healthcare and information, ensuring that all women, regardless of their economic or social status, can pursue preventive health measures. They bridge gaps in the healthcare system and empower women with the knowledge and tools necessary to take control of their health. This support is crucial in building a healthier community and ensuring that preventive care reaches a broader audience.
Health Education and Awareness
Health education is foundational in empowering women to make informed decisions about their health. Educated women are more likely to participate in preventive measures, recognize early signs of health issues, and seek medical advice promptly. “Knowledge is power,” and this knowledge can be lifesaving in health. Women need to understand their bodies and the steps they can take to prevent disease.
Effective educational tools and resources for women might include:
-
Digital platforms like websites and mobile apps offer easy access to health information and self-assessment tools.
-
Workshops and seminars conducted by healthcare professionals that address specific women’s health issues.
-
Printed materials like brochures and flyers distributed in clinics and community centers that provide concise, actionable health information.
-
Social media campaigns raise awareness and educate women on a wide scale about preventive measures and health maintenance.
Through these tools and resources, women can gain the necessary understanding and skills to navigate their health care proactively. Educating women impacts individual lives and fosters a healthier society by promoting widespread health literacy and preventive practices.
Conclusion
This article has highlighted the essential tools of preventive health measures critical for women to maintain and enhance their overall wellness. These include regular health screenings tailored to women’s needs, vaccinations to prevent serious diseases, and nutritional supplements that support bodily functions and prevent deficiencies. Additionally, we’ve explored the importance of mental health assessments, lifestyle modifications, and genetic testing in managing health proactively. Community health initiatives and comprehensive health education are pivotal in empowering women with the knowledge and resources necessary to take control of their health.
Women are encouraged to incorporate these preventive health tools into their regular health regimens. Doing so can significantly improve their quality of life and ensure long-term wellness. Prevention is always better than cure, and by taking proactive steps today, women can safeguard their health for the future.
Call to Action
Take control of your health journey today! Don’t wait for symptoms to tell you something is wrong. Be proactive by scheduling regular screenings, staying updated on vaccinations, and maintaining a balanced diet enriched with the necessary supplements. Remember, your health is in your hands, and taking preventive measures now can lead to a healthier, happier life.
Additional Resources
For further reading and more in-depth information, consider the following resources:
-
American Cancer Society. (2020). Guidelines for the Early Detection of Cancer. https://www.cancer.org/healthy/find-cancer-early.html
Provides guidelines on when and how often women should seek screening for various types of cancer.
-
Office on Women’s Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2019). Women’s Health. https://www.womenshealth.gov/
Offers comprehensive information on a wide range of women’s health issues, including preventive care.
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Vaccines for Women. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/adults/rec-vac/women.html
Details recommended vaccinations for women, tailored by age and health condition.
-
National Osteoporosis Foundation. (n.d.). About Bone Health. https://www.nof.org/patients/what-is-osteoporosis/
Provides valuable insights into maintaining bone health and preventing osteoporosis.
-
World Health Organization. (2018). Mental Health: Strengthening Our Response. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-health-strengthening-our-response
Highlights the importance of mental health care and provides global strategies for improvement.
Explore these resources to deepen your understanding and enhance your ability to manage your health effectively.
